Studland Bay, Dorset
Highlights
The relatively thin
Introduction
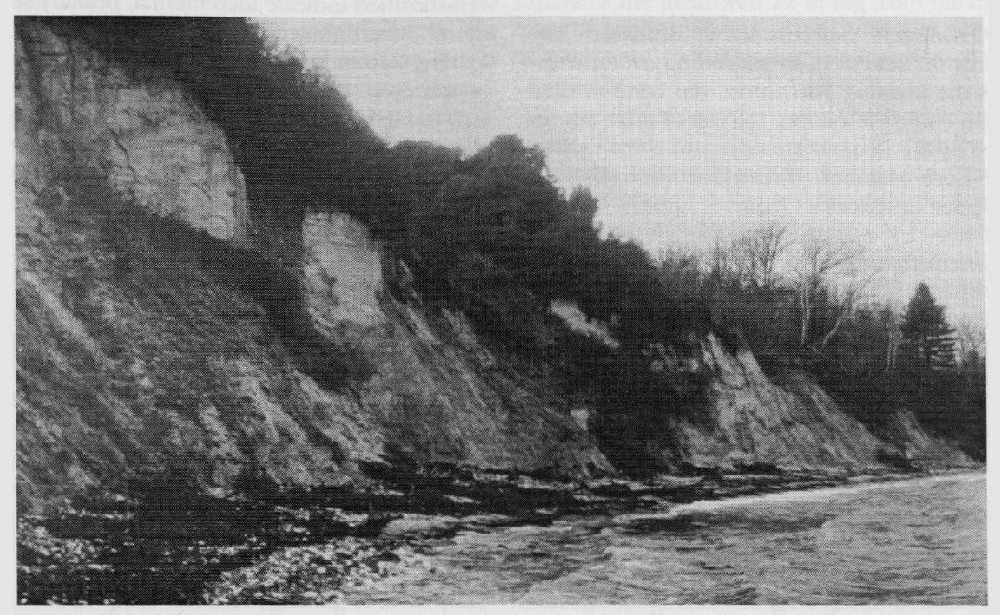
The site extends from the unconformable contact with the Upper Cretaceous Chalk northwards to just beyond Redend Point. Apart from the few instances where sediments of possible Tertiary age infill solution pipes in the Chalk, such as is seen in St Oswald's Bay, to the east of Durdle Door
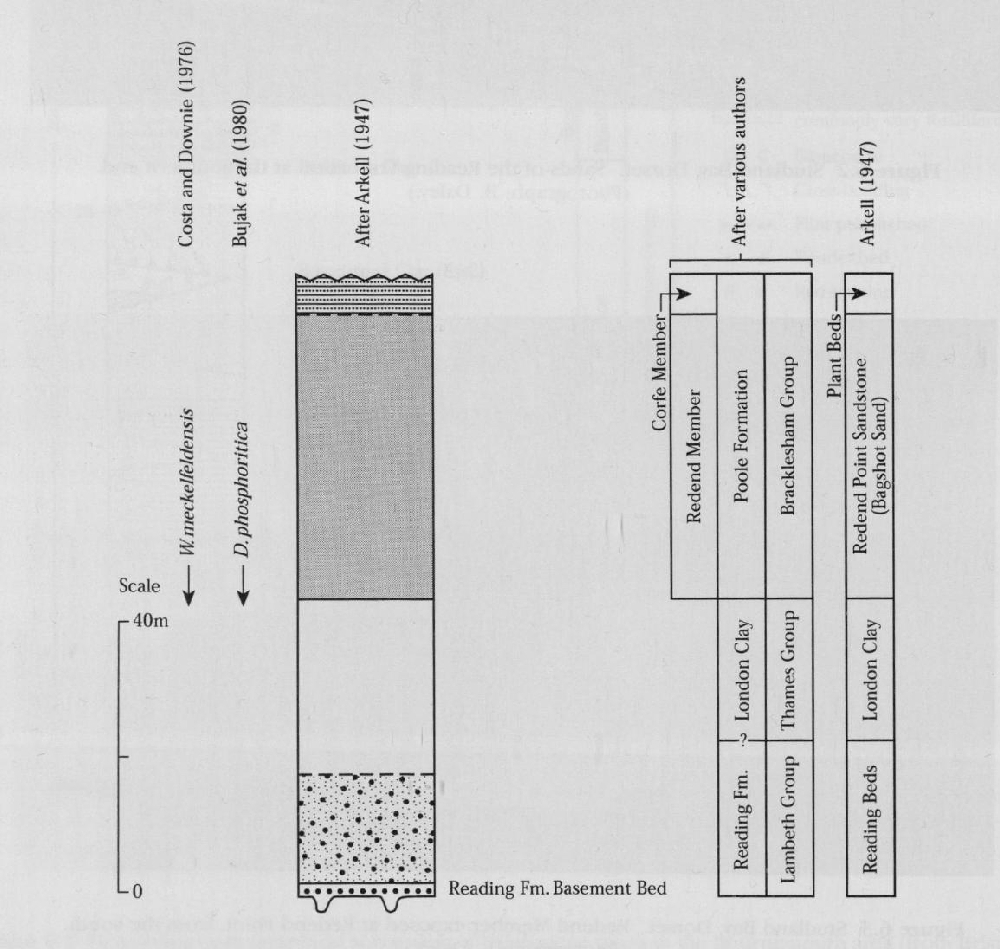
Aspects of Studland were referred to by Lyell (1827) in his pioneer survey of the Tertiary succession in the Hampshire Basin but little was written about it until Monkton (1910) reported a visit by the Geologists' Association. Arkell (1947) gave a more detailed account in which the post-London Clay strata were referred to as the Bagshot Beds.
Little has been published since Arkell's description, with a few exceptions, such as a brief discussion of the plant fossils of the
Although referring to an area to the north and east of this site, the recent Bournemouth Memoir (Bristow et al., 1991) provides considerable information that also assists interpretation here (see
Recently (December, 1998), the author has learned that, following re-mapping by the British Geological Survey, doubts have been expressed as to whether the lithostratigraphical assignment of much of the succession to the
Description
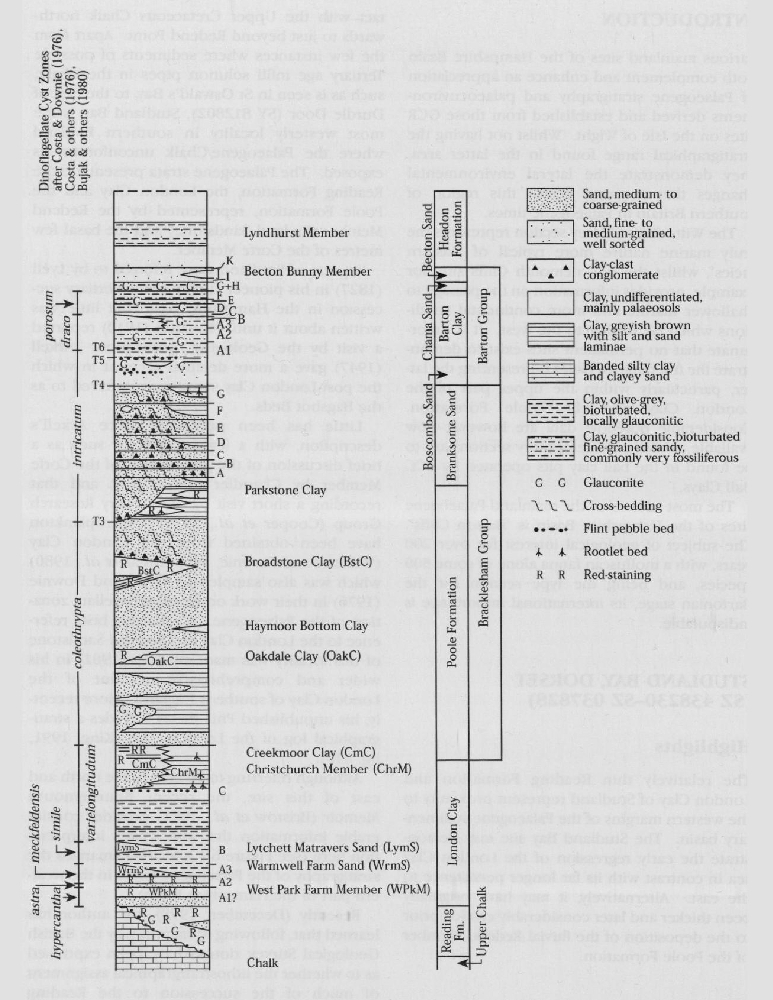
The Palaeogene succession at Studland Bay
The unconformity
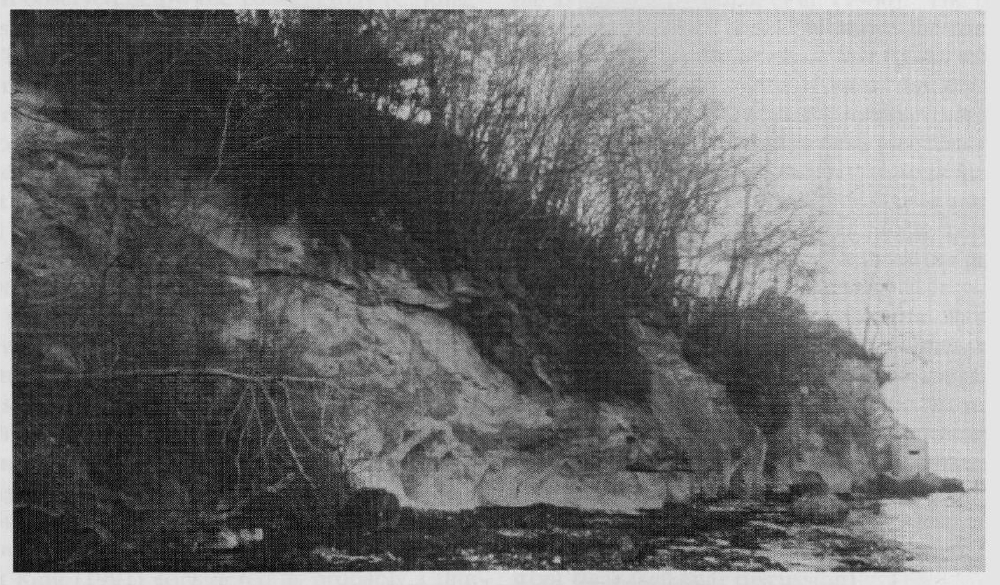
The contact between the Reading Beds and the underlying Chalk is a particularly striking example of the irregular surface which is often associated with this unconformity. Erosional cavities up to 3 m wide and containing Palaeogene material extend down into the underlying Cretaceous strata. Those which are internally well-stratified indicate incremental, primary sediment accumulation. The junction of the
Recent work by the British Geological Survey has shown that the nature of the Chalk/Palaeogene surface in Dorset has in places been affected by tectonism. For example, the hummock of Chalk to the north of the main Chalk outcrop in Studland Bay mentioned by Arkell (1947, p. 221) is now thought to be a fault block (C.M. Barton, pers. comm.).
Lithological succession
Thin basal sands and granule conglomerates of the
Stratigraphy
The lower part of the
The London Clay is very poorly exposed on slumped and strongly vegetated slopes above shore level but King (1991, fig. A16) was able to recognise some 22 m resting on the muds of the
An unexposed interval of uncertain thickness separates the measured 22 m log from the overlying Redend Member and it may be that, at least in part, this includes strata assignable to the London Clay.
Curry et al. (1978) used both the terms Redend Sandstone and Redend Member for the sandstone which succeeds the London Clay at Studland
Biostratigraphy
Bujak et al. (1980) reported dinoflagellate-barren sediments near the base of the London Clay but found material indicative of the Deflandrea phosphoritica dinoflagellate Assemblage Zone (LC–1) 0.9 m from the top of the formation. Costa and Downie (1976, p. 604) collected the zone fossil Wetzeliella meckelfeldensis within 2 m of the top, presumably from the same sample as quoted by Bujak et al. (1980). The position of this sample is c. 17 m above the base of the London Clay (Bujak et al., text-fig. 4), which, if accurate, would place it near the division A/division B boundary. It is probable that they took the sand with a pebbly base (see above) as the base of the 'Bagshot Sands'. In sites further eastwards, in both the Hampshire Basin and the London Basin, the upper part of the London Clay contains younger zone fossils of the genus Wetzeliella (sensu lato).
The stratigraphical affinities of the Redend Member are unclear. The W. meckelfeldensis age of the uppermost London Clay below suggests a possibility that it corresponds to the Warmwell Farm Sand found to the north (cf. Bristow et al., 1991, fig. 8) and whose lateritic cementation is compatible with the limonitization here. However, in the absence of zone fossils, its age and correlation with other strata elsewhere is far from clear (see later discussion).
Sedimentology
The Reading Basement Bed comprises sparsely glauconitic muddy sand. Above, some 15–20 m of cross-bedded, mainly clean, quartzose sands to granule conglomerates with thin beds of silty clay locally containing fragmentary plant material, contrasts with the dominantly argillaceous sequences of Alum and Whitecliff Bays to the east. Clay mineral studies by Gilkes (1968) indicated a predominantly illite–kaolinite composition at Studland. The basal 2 m was, however, exceptional in containing abundant smectite.
Whilst the London Clay is very poorly exposed, its marine origin is supported by the glauconitic nature of its lower part, the presence of Lingula and agglutinating foraminifera. C. King (pers. comm.) considers that the sediments present are similar to those of the London Clay elsewhere and may be interpreted as marine, although calcareous fossils have been destroyed by post-depositional decalcification.
Lithologically, the Redend Member comprises relatively well-lithified, fine to medium sandstones. These are essentially clean, well-sorted sands, now strongly limonitized. King (1981, p. 91) considered that the base is 'certainly marine', whilst suggesting that the upper part, with several fining-upwards cycles, is fluvial in origin.
Parallel-laminated, sometimes lignitic, sands and black sandy muds follow the Redend Member. Cooper et al. (1976) noted the abundance of plant fragments, and whilst referring this unit to the Pipeclay Series of Arkell (1947) (the
Macroflora
Chandler (1962, p. 4) referred in somewhat more detail than Cooper et al. (1976) to the plant macrofossils of the
Interpretation and evaluation
Studland Bay is the most westerly site in the Hampshire Basin to show the contact between the Cretaceous and the Palaeogene, together with an overlying succession of Palaeocene and lower Eocene strata. Hence, the succession here provides some insight into the palaeogeographical development towards the western end of the Hampshire Basin in early Palaeogene times. Other data which could throw light on the development of the remainder of the Palaeogene succession in this area have arisen from the local exploration and exploitation of ball clay but some of this information is commercially 'sensitive' and not in the public domain.
Comparison with other localities
Compared with the sections in Whitecliff Bay and Alum Bay on the Isle of Wight, that at Studland is limited in stratigraphical range but it demonstrates both similarities with and differences from the Palaeogene successions found further to the east.
Rounded pebbles and the presence of glauconite at the bottom of the
Compared with more easterly localities, there is only a thin development of the London Clay at Studland and it is clear that it is essentially the younger part of the formation that is absent. In this regard, the discovery by Costa and Downie (1976) of W meckelfeldensis within 2 m of the top of the London Clay here is particularly significant, for at Alum Bay D. similis occupies this position, with the even younger D. varielongituda at the top of the formation (sensu King, 1981) in Whitecliff Bay. Costa and Downie (1976) suggested that such a lateral change is a clear indication of the diachronous nature of the top of the London Clay, the consequent inference being that a regressive development began much earlier in this more westerly area. C. King (pers. comm.) believes now that the top of the London Clay may not have been diachronous and that its attenuated succession in Studland Bay may have resulted from erosion in this area prior to deposition of the
Depositional environment and palaeogeography
The concentration of smectite in the
Above the
Since the London Clay is so poorly exposed at Studland, discussion must inevitably be limited. It is, however, far thinner here than further to the east, an indication that the Studland area represents the western margin of the London Clay sea. Indeed, some of the palynomorphs recently found by BGS in the Studland Bay section are paralic in character rather than marine as in the London Clay further east (J.B. Riding, pers. comm.). There is some indication that, in some places, the London Clay was subaerially exposed relatively soon after deposition since, in the north-western part of the Bournemouth District (sensu BGS), strata formerly considered as 'Reading Beds' are now thought of as pedogenically reddened London Clay, the latter resting directly on the Chalk (Bristow et al., 1991, p. 20).
Costa and Downie (1976) suggested a major unconformity at the base of the Redend Sandstone. Although King (1981, p. 91) originally felt that this was unlikely, he now is inclined to agree (pers. comm.). Having earlier (1981) thought that this unit was probably correlatable with higher horizons in the London Clay further to the east, he now considers it to be part of a fluvial succession younger than the London Clay. However, since the unit has, as yet, yielded no zone fossils, its age remains uncertain. It is unfortunate that Townsend and Hailwood (1985) did not include Studland in their revealing magnetostratigraphical work on the Palaeogene, since this might very well have shed more light on this problem.
Recent alternative lithostratigraphical interpretation
Recent re-mapping of this part of Dorset by the British Geological Survey (BGS) (Sheet 342/343, Swanage, in press) has led to an alternative lithostratigraphical interpretation of the Studland Bay section incompatible with the assignment of the succession to the
The suggestion that the London Clay is absent in the Studland Bay section is not supported by evidence of its occurrence found by King (1991). Clearly further investigation is necessary to resolve the apparent incompatibility of the two interpretations. As this account goes to press, BGS is about to re-evaluate the palynofloral evidence (J.B. Riding, pers. comm.). This may turn out to be very revealing since the palynomorphs found by BGS did not preclude the presence of the London Clay on biostratigraphical grounds but were thought to represent a different, more paralic, biofacies than that which characterized the typically marine London Clay farther to the east.
Conclusions
Although stratigraphically limited in extent, the Studland section is important in that it throws light on the palaeogeography of Palaeocene and early Eocene times towards the western end of what is now the Hampshire Basin.
Both the
The fluvial Redend Member, unrepresented at more easterly localities, may correlate with younger parts of the London Clay elsewhere to the east but alternatively may be younger than the latter and separated from it by an unconformity.